CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
The central nervous system is divided into two major parts: the brain and the spinal cord.
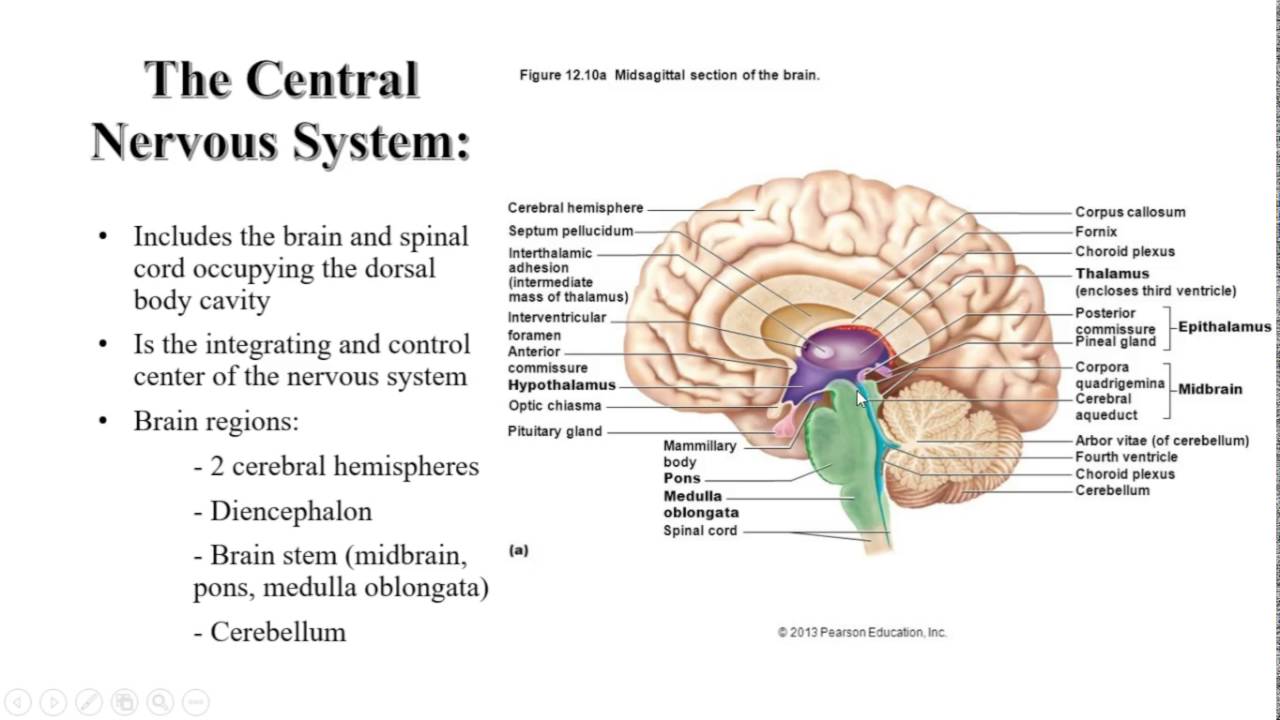

Firstly,we are going to talk about the brain.
Parts of the Human Brain and their Subdivisions
Human encephalon resembles, in structure and function, with that of the other vertebrates. The scientists reveal that parts of the human brain are Forebrain, Midbrain & Hindbrain and the related structures that collectively act as a single highly specialized unit. These parts work in coordination and perform different functions of brain. More specifically, it is divided into five major regions, namely, telencephalon, diencephalon or inter-brain, myelencephalon (hindbrain/medulla oblongata), metencephalon and mesencephalon (midbrain). Here follows a precise but comprehensive description of each of the above given divisions.
Telencephalon/Cerebrum—Anterior Part Of Forebrain
Further composed of cerebral cortex, limbic and basal ganglia, it is the superior-most part of the vertebrate CNS (Central Nervous System) and is divided into two symmetrical left and right regions called cerebral hemispheres. In controlling the deliberate or voluntary activities in the body, as its primary function, it takes the help of another brain division, the cerebellum. In the advanced mammalian species, the ridges (gyri) and furrows (sulci) serve to increase the surface area of cerebral cortex without occupying much volume. The primary human brain functions performed by telencephalon include language & communication, body movements, olfaction, learning & memory, sensory perception, and so on.
Diencephalon/Inter-Brain—Posterior Part Of Forebrain
The anterior structures of front part of your brain consist of cerebrum, while the posterior ones are contributed by interbrain that forms a region of the vertebrate neural tube at the upper portion of the brain-stem. Thalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus and hypothalamus are the four sub-divisions. Here Hypothalamus is one of the parts of the human brain that initiates, coordinates, maintains and assists in the successful accomplishment of a number of visceral activities with the help of its hormonal secretions. Moreover, the sensory Optic Nerve, coming from the eye through optic canal, gets attached to the diencephalon and plays a role in vision.
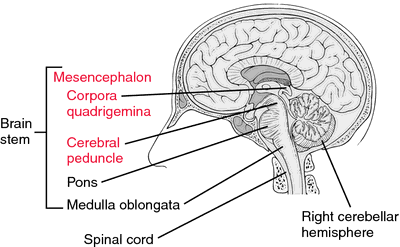
Mesencephalon/Midbrain
Anatomically comprised of cerebral penuncles, tegmentum, tectum and a number of fasciculi and nuclei, it forms the middle region of brain and an important part of Central Nervous System (CNS). It performs a number of individual tasks of vital importance, namely, wake/sleep, alarming, motor control, hearing, vision and the regulation of body temperature. On its anterior end, it is connected with forebrain and on the posterior end, it is attached to metencephalon (or pons), thus placed near the center of your brain. Substantia nigra, a sub-division of the mesencephalon, is involved in the production of physiologically very important organic compound, called dopamine that plays the role of habituation and motivation in species ranging from humans to the members of phylum insecta.
Metencephalon—Anterior Part Of Hindbrain
Composed of cerebellum, pons, different nerves and fourth ventricle, it is an important portion of the developmental division of your brain and performs vital functions associated with Central Nervous System (CNS), viz. muscle movements, sleep, circulation, balance, arousal and cardiac reflexes. If you want to know about the wonderful working of different parts of brain, just go through the interesting human brain facts.

Myelencephalon/Medulla Oblongata—Posterior Part Of Hindbrain
Forming an important subdivision, it is the lower most part of your brain that serves to mutually connect the two major structures of CNS, namely, brain and the spinal cord. Medulla oblongata is comprised of the lower part of brainstem (or hindbrain) and contains different control centers, viz. vomiting, cardiac, vasomotor and respiratory to conduct various autonomic and involuntary activities in the body, like, breathing, blood pressure, heart-beat rate, and so on. Any of the diseases of human brain affecting this part will make it unable to perform the given functions appropriately.

THE SPINAL CORD
The spinal cord is along tube like structure which extends from the brain. The spinal cord is composed of a series of 31 segments. A pair of spinal nerves comes out of each segment. The region of the spinal cord from which a pair of spinal nerves originates is called the spinal segment. Both motor and sensory nerves are located in the spinal cord.
The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult women and 45 cm long in adult men and weighs about 35-40 grams. It lies within the vertebral column, the collection of bones (back bone).
Other Parts of Central Nervous System
The meninges are three layers or membranes that cover the brain and the spinal cord. The outermost layer is the dura mater. The middle layer is the arachnoid, and the innermost layer is the pia mater. The meninges offer protection to the brain and the spinal cord by acting as a barrier against bacteria and other microorganisms.
The Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) circulates around the brain and spinal cord. It protects and nourishes the brain and spinal cord.


Comentarios
Publicar un comentario